No circuito de reset do STM32 mostrado na Figura 1, um diodo de comutação é geralmente conectado em paralelo com o terminal resistivo do circuito de reset RC. A principal função desse diodo é acelerar a liberação da carga do capacitor.
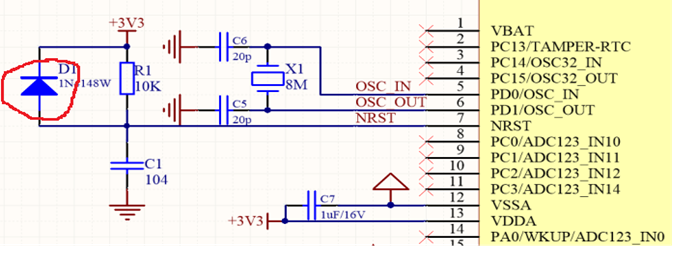 Figura 1 Circuito de reset do STM32
Figura 1 Circuito de reset do STM32
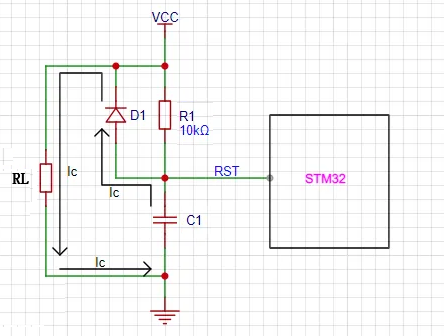 Figura 2. Circuito de descarga do circuito de reset do STM32
Figura 2. Circuito de descarga do circuito de reset do STM32
Em um circuito de reset RC, um diodo de descarga é indispensável, sendo sua principal função a descarga rápida. Quando a energia é desligada ou ocorre uma queda momentânea de energia devido a interferência, a carga armazenada no capacitor precisa ser liberada por algum caminho para garantir o reset adequado na próxima vez que a energia for ligada. Sem um diodo, quando o pulso de interferência da queda de energia é curto, o capacitor descarrega através do resistor R1, que possui uma alta resistência, resultando em uma baixa velocidade de descarga. O circuito RC não consegue descarregar completamente no momento da falha de energia, e o sistema não consegue reiniciar automaticamente após o restabelecimento da energia. A interferência da queda momentânea de energia pode fazer com que o programa pare de funcionar normalmente, levando a um comportamento errático ou à entrada em um loop infinito. A adição de um diodo fornece um caminho de descarga rápida para o capacitor. Devido à baixíssima resistência de condução do diodo, como mostrado no caminho de descarga do circuito de reset do STM32 na Figura 2, a carga no capacitor C1 descarrega rapidamente através do diodo D1, garantindo a estabilidade e a confiabilidade do circuito de reset. Quando a energia é desligada, o capacitor descarrega rapidamente para o terra através do diodo. Quando a energia é restaurada, o capacitor já está completamente descarregado e pode iniciar imediatamente o processo de carga, acionando a operação de reinicialização. Esse processo de descarga rápida garante que o circuito de reinicialização possa retornar rapidamente ao seu estado inicial após uma queda de energia ou fornecimento de energia anormal.

Xml política de Privacidade blog Mapa do site
Direitos autorais
@ Micro-Magic Inc Todos os direitos reservados.
 SUPORTADO POR REDE
SUPORTADO POR REDE
